WordPress came onto the market with its first release in May 2003. Founded by Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little
WordPress is a free and open-source content management system written in PHP and paired with a MySQL or MariaDB database. Features include a plugin architecture and a template system, referred to within WordPress as Themes.








WordPress is a free and open-source content management system written in PHP and paired with a MySQL or MariaDB database. Features include a plugin architecture and a template system, referred to within WordPress as Themes.


In May 2004, version 1.2 of WordPress came with plugin architecture. This enabled users and developers to extend the functionality of WordPress by writing their own plugins and sharing them with rest of the community.
As WordPress was opening itself to the community, something totally opposite was happening in the blogging industry at that time.
The market leader in blogging tools industry at that time was Moveable Type. They announced new licensing terms which were not liked by many of their users. This forced many of their users to look for a new blogging platform.
WordPress 1.2, presented itself as an ambitious project offering users a mature, stable, easy and flexible platform with features that rivaled their proprietary competitors. The adaption rate of WordPress skyrocketed with this release.

With the increase in the number of users, WordPress started getting better with the help and interest of the community.
In February 2005, WordPress 1.5 came with Pages, comment moderation tools, new default theme Kubrick, and a completely new Theme System. Matt announced themes with these words:
In 1.5 we have created an incredibly flexible theme system that adapts to you rather than expecting you adapt to it. You can have your entire weblog run through a single file, just like before, or you can literally have a different template for every single different category. It’s as much or as little as you want. We’ve also broken common site elements like headers, footers, and sidebars into their own files so you can make a change in one place and see it everywhere immediately. “Matt Mullenweg – Announcing WordPress 1.5”

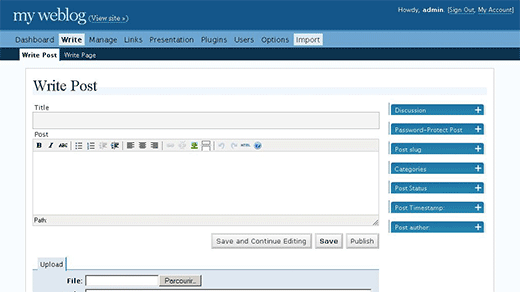
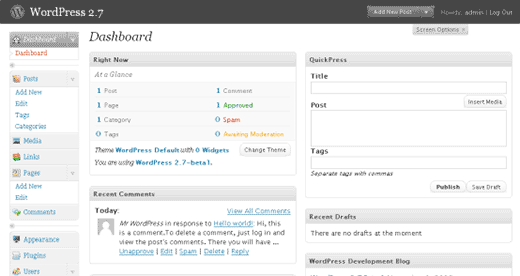
In December 2005, WordPress 2.0 was released with a new admin dashboard. This new admin area was a complete overhaul of the administration screens in WordPress.
It used JavaScript and DHTML to make a better user interface where users did not need to load a page to perform some simple tasks. Users were now able to add categories and tags to posts without leaving the post editor or delete comments without reloading the comments screen.

The shiny new admin UI was not the only significant improvement in this release.
It was the first release that came with Akismet anti-spam plugin pre-installed. It also came with a WordPress database backup plugin, wp-db-backup, which was then dropped in 2007. Another first for this release was the introduction of a functions.php file in the Theme System.
On March 1, 2006, Automattic, the company founded by WordPress co-founder Matt Mullenweg, filed the trademark registration for WordPress and WordPress logo.
In 2008, a web design company called Happy Cog joined the WordPress project to help design a new WordPress admin interface. A usability study was conducted to design the admin UI.
Throughout the year new features such as shortcodes, one-click updates, and built-in plugin installation were added to WordPress with different releases.

In June of 2010, Automattic, the company founded by WordPress co-founder Matt Mullenweg, transferred the ownership of WordPress trademark and logo to the WordPress Foundation. This was a significant moment in WordPress history, because it ensured that WordPress will continue to grow, and is not dependent on a company or a group of developers to continue the project.
On June 17, 2010, WordPress 3.0 was released. It was a major step towards WordPress as CMS. This release introduced several features such as custom post types, better custom taxonomies, custom backgrounds, header, menus, contextual help on admin screens, etc. WordPress MU project was merged into WordPress core to create Multisite networks.
In 2011, Post formats and admin bar made their way into WordPress.
Around that time, some really cool WordPress plugins were building powerful eCommerce platforms on top of WordPress. This enabled WordPress users to create online stores and build powerful ecommerce websites using WordPress.
In 2012, theme customizer, theme previews, and new media manager were introduced. These features tremendously helped new users in creating image galleries and previewing themes before they change to a new theme.
In 2013, WordPress 3.7 came with the new automatic updates feature that allowed WordPress to automatically update your site’s software for minor releases. The automatic updates feature is very similar to what Google Chrome browser does. Several users didn’t like the feature, so we wrote a tutorial on how to disable automatibecometes.
By this time WordPress had already became the most popular CMS in the world.
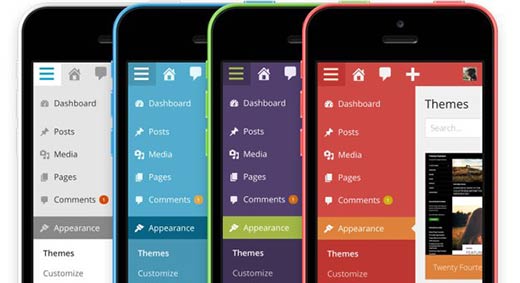
In December 2013, WordPress 3.8 was released which introduced MP6, the new WordPress admin interface. This new interface was responsive and was aimed to provide a better user experience to users, on any device or screen size.

On April 16, 2014, WordPress 3.9 was released. It focused on improving the WordPress visual post editor. Images can now be dragged and dropped directly into the post editor. Users are now able to edit images right inside the editor and see their gallery previews inside the editor. WordPress 3.9 also introduced live widget previews, audio playlists, and several other enhancements.



In May 2004, version 1.2 of WordPress came with plugin architecture. This enabled users and developers to extend the functionality of WordPress by writing their own plugins and sharing them with rest of the community.
As WordPress was opening itself to the community, something totally opposite was happening in the blogging industry at that time.
The market leader in blogging tools industry at that time was Moveable Type. They announced new licensing terms which were not liked by many of their users. This forced many of their users to look for a new blogging platform.
WordPress 1.2, presented itself as an ambitious project offering users a mature, stable, easy and flexible platform with features that rivaled their proprietary competitors. The adaption rate of WordPress skyrocketed with this release.

With the increase in the number of users, WordPress started getting better with the help and interest of the community.
In February 2005, WordPress 1.5 came with Pages, comment moderation tools, new default theme Kubrick, and a completely new Theme System. Matt announced themes with these words:
In 1.5 we have created an incredibly flexible theme system that adapts to you rather than expecting you adapt to it. You can have your entire weblog run through a single file, just like before, or you can literally have a different template for every single different category. It’s as much or as little as you want. We’ve also broken common site elements like headers, footers, and sidebars into their own files so you can make a change in one place and see it everywhere immediately. “Matt Mullenweg – Announcing WordPress 1.5”

In December 2005, WordPress 2.0 was released with a new admin dashboard. This new admin area was a complete overhaul of the administration screens in WordPress.
It used JavaScript and DHTML to make a better user interface where users did not need to load a page to perform some simple tasks. Users were now able to add categories and tags to posts without leaving the post editor or delete comments without reloading the comments screen.

The shiny new admin UI was not the only significant improvement in this release.
It was the first release that came with Akismet anti-spam plugin pre-installed. It also came with a WordPress database backup plugin, wp-db-backup, which was then dropped in 2007. Another first for this release was the introduction of a functions.php file in the Theme System.
On March 1, 2006, Automattic, the company founded by WordPress co-founder Matt Mullenweg, filed the trademark registration for WordPress and WordPress logo.
In 2008, a web design company called Happy Cog joined the WordPress project to help design a new WordPress admin interface. A usability study was conducted to design the admin UI.
Throughout the year new features such as shortcodes, one-click updates, and built-in plugin installation were added to WordPress with different releases.

In June of 2010, Automattic, the company founded by WordPress co-founder Matt Mullenweg, transferred the ownership of WordPress trademark and logo to the WordPress Foundation. This was a significant moment in WordPress history, because it ensured that WordPress will continue to grow, and is not dependent on a company or a group of developers to continue the project.
On June 17, 2010, WordPress 3.0 was released. It was a major step towards WordPress as CMS. This release introduced several features such as custom post types, better custom taxonomies, custom backgrounds, header, menus, contextual help on admin screens, etc. WordPress MU project was merged into WordPress core to create Multisite networks.
It also came with Twenty Ten, which started the tradition of a new default theme for each year.
In 2011, Post formats and admin bar made their way into WordPress.
Around that time, some really cool WordPress plugins were building powerful eCommerce platforms on top of WordPress. This enabled WordPress users to create online stores and build powerful ecommerce websites using WordPress.
In 2012, theme customizer, theme previews, and new media manager were introduced. These features tremendously helped new users in creating image galleries and previewing themes before they change to a new theme.
In 2013, WordPress 3.7 came with the new automatic updates feature that allowed WordPress to automatically update your site’s software for minor releases. The automatic updates feature is very similar to what Google Chrome browser does. Several users didn’t like the feature, so we wrote a tutorial on how to disable automatibecometes.
By this time WordPress had already became the most popular CMS in the world.
In December 2013, WordPress 3.8 was released which introduced MP6, the new WordPress admin interface. This new interface was responsive and was aimed to provide a better user experience to users, on any device or screen size.

On April 16, 2014, WordPress 3.9 was released. It focused on improving the WordPress visual post editor. Images can now be dragged and dropped directly into the post editor. Users are now able to edit images right inside the editor and see their gallery previews inside the editor. WordPress 3.9 also introduced live widget previews, audio playlists, and several other enhancements.
More refinements were made to WordPress core throughout the year with subsequent WordPress 4.0 and WordPress 4.1 releases.
2014 was also the first year when non-English downloads for WordPress surpassed English downloads.
In 2015, WordPress 4.2, 4.3, and 4.4 were released. These releases focused on improved localization, emoji support, theme customizer, and laying down infrastructure for the WordPress REST API.

In the same year, WooCommerce, the most popular WordPress eCommerce plugin was acquired by Automattic (the company founded by WordPress co-founder Matt Mullenweg).
In 2016, WordPress 4.5, 4.6, and 4.7 were released. Each release introduced some new features and improvements. Most notable changes during the year were streamlined updates for plugins and themes, content recovery by using browser storage, and custom css feature for theme customizer. By the end of the year, WordPress.org announced actively supporting HTTPs
In 2017, WordPress 4.8 and 4.9 were released. These releases brought several new default widgets to add audio, video, images, gallery, rich text, and HTML. These releases also laid the groundwork for the new WordPress block editor.
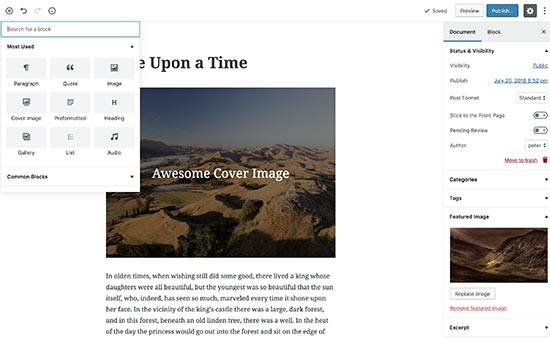
In 2018, WordPress 5.0 was released with a brand new editing experience. The new WordPress block editor project was codenamed Gutenberg. See our complete Gutenberg tutorial – WordPress block editor.
The story of WordPress tells us how open source communities work to make something so useful without compromising software freedom. WordPress project is driven by a community of dedicated developers, users, and supporters (Related: Why is WordPress free?).
WordPress started out because the development of an existing blogging software b2/cafelog was discontinued by their main developers. In 2003, two users of b2/cafelog, Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little, decided to build a new platform on top of b2/cafelog.
They probably didn’t know that they are about to start a journey that would eventually benefit millions of users around the globe, create thousands of jobs, and a whole industry of developers, designers, writers, bloggers, and web publishers would make their living off it.
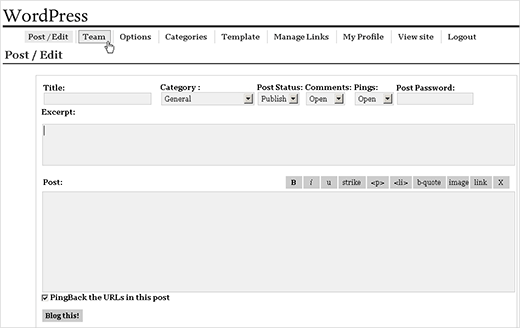
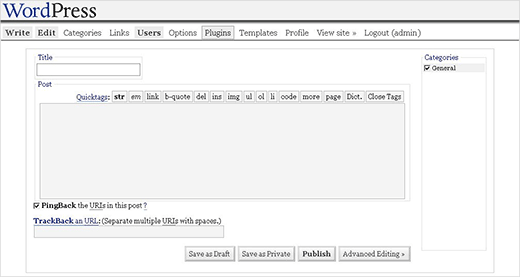
On May 27, 2003, Matt announced the availability of the first version of WordPress. It was well received by the community. It was based on b2 Cafelog with significant improvements. The first version of WordPress included a new admin interface, new templates, and generated XHTML 1.1 compliant templates. The post editor looked lik
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment